What is a WiFi Booster and How Does it Work?
How to Boost WiFi Signal?
If you struggle with maintaining a reliable WiFi connection throughout your house, a WiFi booster might help! Though, they don’t actually boost WiFi signals. So, what is a WiFi booster and how does it work?
Installers and Integrators
Take advantage of our system design and installation services. Learn more or call us for a free consultation: 1-800-969-8189
What is a WiFi Booster?
Also known as a wireless network extender or WiFi repeater, WiFi boosters extend the range of your WiFi signal. This helps eliminate dead zones and improve connectivity in weak signal areas. Thus, giving the illusion of a boosted network.
There are a variety of WiFi boosters available. They vary in design, range, and frequency band usage.
- Design: Most WiFi boosters are designed to plug into a wall outlet. Others can be placed on flat surfaces like a desk, table, or shelf.
- Range: Routers tend to have a range of 150-300 feet. Any device on the edge or outside the router's coverage area will experience connectivity issues. Depending on the model, WiFi boosters can increase the range of your WiFi network by 1,200-12,000+ sq ft.
- Frequency Bands: WiFi boosters are typically single or dual-band. Single-band units utilize one frequency band (2.4GHz or 5GHz) to transmit data, while dual-band units use both frequencies. Some WiFi boosters designed with mesh technology are tri-band. They support 2.4, 5, and 6GHz.
How Does a WiFi Booster Work?
WiFi boosters connect to your WiFi router to create a bridge. They receive WiFi signals and rebroadcast them into those difficult-to-reach areas.
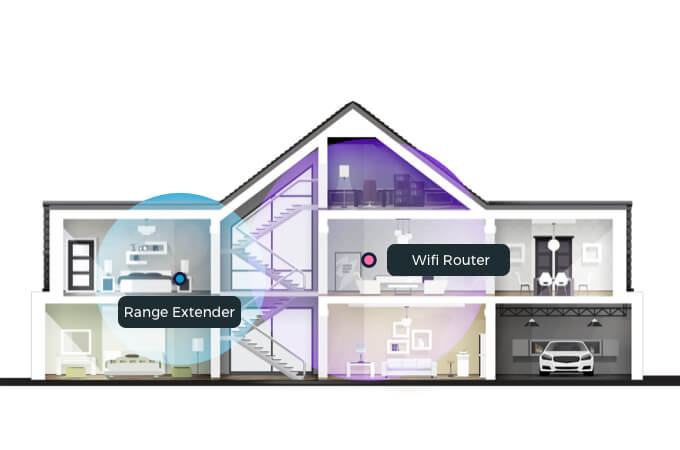
Installation is pretty straightforward. In many cases, all you have to do is press the WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) button on your router and WiFi booster. Of course, setup will vary across manufacturers (Netgear, Tp-Link, Linksys, D-Link, Asus, Orbi, Eero, etc.).
For optimal results, placement is extremely important. The WiFi booster must be close enough to your router to receive a decent signal, but far enough away to cover your desired areas.
Once installed, most WiFi boosters create a second network – the extended network. You’ll need to connect your laptop, phone, tablet, and other smart devices to the extended network to benefit from the boosters signal.
What’s the Difference Between a WiFi Booster and WiFi Extender?
There is a lot of confusion revolving around these two terms. Some articles say that a WiFi booster boosts and extends WiFi signal, while WiFi extenders just extend WiFi signal. But as mentioned, WiFi boosters don't actually boost WiFi. While confusing, WiFi booster is simply a different way of saying WiFi extender or WiFi repeater.
Should I Get a WiFi Booster?
If there are areas in your home that don’t get WiFi signal or have slow WiFi, you will definitely benefit from a WiFi booster. They are best for multiroom to spot coverage. If you find that one WiFi booster will not be enough, rather than opting for multiple, consider a WiFi mesh network. Visit our blog on WiFi Boosters vs Mesh Networks for more information.
Here are great WiFi booster options:
TP-Link AC1200 WiFi Extender
- Dual Band, 5 GHz & 2.4 GHz
- Covers Up to 1,500 Sq Ft
- One Ethernet Port
- Supports Up to 30 Devices
- Simple Installation
The TP-Link AC1200 WiFi Extender is compatible with any WiFi router and offers up to 1,500 sq ft of coverage. It can connect up to 30 devices and provide dual-band speeds up to 1,200 Mbps. Once installed, your WiFi will reach places it couldn't before. This range extender is great for homes and offices.
Macard WiFi Booster
- 2.4 GHz Processor
- Covers Up to 9,000 Sq Ft
- One Ethernet Port
- Supports Up to 45 Devices
- Easy Setup
Mercard’s WiFi Booster offers up to 9,000 sq ft of coverage. Whether you live in an apartment or a large home, Mercard has you covered. It’s boasted as the most powerful WiFi extender. Ultra-high bandwidth allows for up to 45 connected devices.
Are There WiFi Booster Alternatives?
In addition to a mesh network, a powerline adapter is a great alternative.
Unlike WiFi boosters, powerline adapters use the electrical wiring in your home to extend the WiFi signal.
Powerline kits are composed of two adapters. One plugs into a power outlet near the router and the other in the area where you need signal. You’d connect the first adapter to the router via an ethernet cable and the second to an ethernet device.
Once set up, the internet signal will travel through the electrical wiring and provide the wired devices with a reliable connection. In addition, the second adapter in some kits also broadcasts a wireless signal to extend the WiFi range.
TP-Link AV2000 Powerline Adapter
- High-Speed Data Transfer, Up to 2000 Mbps
- Two Gigabit Ports
- Plug and Play Installation
- Built In Power Socket
- Wired and Wireless Network Extension
FAQs
Do WiFi Boosters Really Work?
Yes.
As long as they’re installed correctly, WiFi boosters will improve your WiFi signal's range.
For best results, don’t hide it behind furniture or place it near appliances that can interfere with the signal. Doing so can decrease range and power, which might cause unsatisfactory results.
Do WiFi Boosters Only Work with Wireless Devices?
No.
WiFi boosters work with wireless and wired devices. Most are designed with at least one ethernet port that can be used for printers, computers, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and more. With a wired connection, you can achieve better speeds.
How Do I Know if My WiFi Booster is Working?
Experiencing better connectivity in areas where it was difficult to do so before is a clear sign that it’s working.
If you prefer quantitative proof, speed tests are great tools that can be used to analyze WiFi signal improvements. You’ll need to take pre-installation and post-installation speed tests.
Do WiFi Boosters Increase Internet Speed?
Not exactly. The speed you receive from your internet service provider (ISP) is the bottleneck. A WiFi booster will not boost those speeds further. It’ll simply improve your WiFi reception and coverage, allowing you to experience better speeds in areas where it was difficult to keep connected.
Are WiFi Boosters Secure?
WiFi boosters use the same level of security as WiFi routers - WEP, WPA, and WPA2, with WPA/WPA2 being more secure. In 2019 a new security protocol was introduced known as WPA3. The new protocol improved the security features within public and private WiFi networks, making it more difficult for hackers to access your wireless network.
Contact Signal Boosters Today!
Signal Boosters is a leading provider of cell phone signal boosters and WiFi solutions. We can help you eliminate cellular or Wi-Fi-related signal issues that fit your budget. Give us a call at 1-800-470-6777 with any questions you may have.
Interested in Learning More? Check Out Our Cellular Info Hub / WiFi Info Hub
Disclaimer: This blog contains affiliate links, which means that if you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission. However, this does not affect the integrity or quality of the recommendations provided.











