What is a WiFi Mesh Network and How Does it Work?
Improve Your Home WiFi Coverage with a Mesh Network
Many of us pay for high-speed internet, only to be disappointed by unreliable WiFi in certain rooms. This frustration is common with traditional single routers, which struggle to deliver a strong signal throughout your entire home. For that, a mesh network can be your solution.
Installers and Integrators
Take advantage of our system design and installation services. Learn more or call us for a free consultation: 1-800-969-8189
What is a Mesh Network?
A mesh network is a system of multiple access points designed to blanket your entire home or business with WiFi coverage.
The access points are called mesh nodes, extenders, or satellites. Each node is like a WiFi router. They work together to efficiently route data to and from connected devices in your building.
So unlike with a single router, these nodes create multiple points of connectivity. This ensures you receive the fastest and most reliable connection for your devices, no matter where you are in your home or business.
How Does WiFi Mesh Work?

WiFi mesh networks use multiple mesh nodes. One connects to your modem, acting as the main router. The other nodes sit throughout your house near a power source, wirelessly relaying the signal from the main node and each other.
This creates a wider, stronger WiFi blanket with fewer dead spots. Devices automatically connect to the closest node.
It’s almost like having multiple WiFi routers in your home sharing one seamless WiFi network.
The network topology can be full or partial mesh. A full mesh network means all nodes can communicate with each other. A partial mesh network consists of nodes that can only communicate with certain nodes.
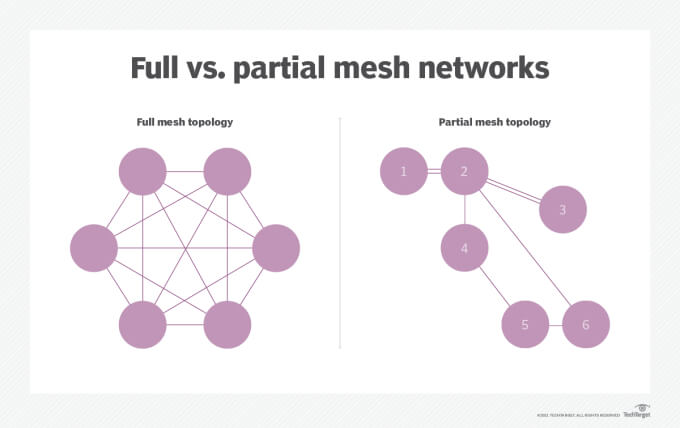
Image Source: TechTarget
Regardless of your setup, data jumps from node to node till it reaches its destination, be it the mesh router or a WiFi device. Built-in smart technology tells the nodes how to route data. They use adaptive routing (aka dynamic routing) technology to choose the fastest and safest path to send and receive information. If a node gets congested or stops working, the network automatically reroutes all the data through a different path to keep you connected.
Can Mesh Network be Wired?
Some mesh systems allow for Ethernet backhaul, which is a fancy way of saying the backbone of your network is composed of wires.
To effectively hardwire your WiFi mesh system, make sure all nodes have at least one Ethernet LAN port. Without it, a wired mesh network isn’t possible
The mesh router would connect to the modem like normal through the WAN port. If your home has built-in hardware infrastructure, you'd use the LAN port to connect your nodes to an ethernet wall socket. For homes that aren't pre-wired, mesh nodes would have to be connected to the LAN ports of a switch that is wired to the mesh router.
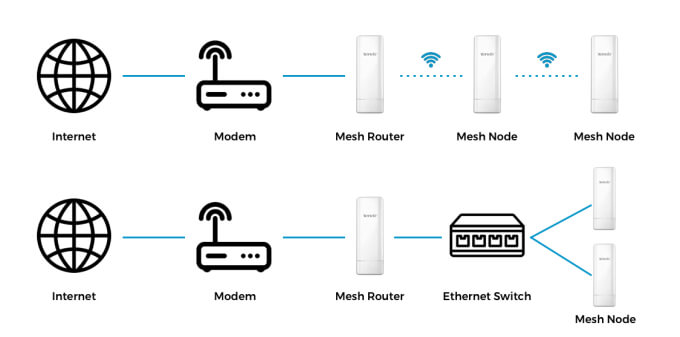
Wiring a mesh network results in better speeds and connection performance. Using Ethernet cables helps route information faster and mitigates signal interference.
To learn more about the differences between ethernet and WiFi, visit The Differences Between Internet, Ethernet, WiFi, and Cellular.
Mesh WiFi vs Traditional WiFi: What's the Difference?

Traditional WiFi networks are centralized, meaning all devices connect to a single router. This can lead to weak signal areas and dead spots in larger homes, especially with WiFi obstructions.
Mesh networks, on the contrary, are decentralized in nature. They offer multiple points of connectivity throughout your home, creating a blanket of strong WiFi and eliminating dead spots. This setup allows for greater coverage and data throughput.
A traditional WiFi network is best for smaller spaces. To achieve whole-home coverage in large areas, mesh networks are the way to go.
What are the Benefits of a Mesh Network?
1) Wider Coverage
With multiple points of connectivity, WiFi signals can reach more places.
2) Easy Setup and Usability
Most mesh networks come with user-friendly apps that assist you in the installation process and allow you to monitor the system. You're able to test speed, create guest networks, monitor connections between points, remove users from the network, add parental controls, and more.
3) Seamless Connection
Mesh WiFi is one large WiFi network. Even though it consists of multiple access points, the system only has one network name and one password. Wireless devices automatically connect to the closest node without having to manually change network connections. There are other networking units, range extenders for example, that create a second network. This forces you to switch between two networks depending on where you are in your home.
4) Flexible and Expandable
It's extremely easy to add extra nodes to expand coverage into those hard-to-reach areas for a reliable WiFi connection. If needed, you can also easily remove or rearrange the nodes.
5) Technology that Self-Heals
If you need to add, remove, or rearrange nodes, the system automatically configures itself to find the best routes to send and receive information. Additionally, if a node stops working, the system will self-heal and re-route all data through the most efficient path.
6) Better Stability
Your network does not depend on a single point for reliable connectivity. If that single point crashes or gets overloaded, the whole network suffers. With a mesh network, there are multiple routes data can travel through, increasing stability. If one node fails, data continues to flow.
7) Simple Infrastructure
Being wireless, mesh networks do not require much infrastructure. All you need are power sockets and a cable to connect the mesh router to the modem.
8) Aesthetic Design
Many who have traditional routers or extenders hide them because they can be an eyesore. Mesh networks are designed to match your home décor. You won’t have to tuck them away in a closet, drawer, or behind furniture. To make mesh nodes more appealing, some models feature smart speakers powered by virtual assistant technology like Google Assistant and Alexa.
9. Secure
Mesh systems use WPA2 or WPA3 privacy encryptions; these are the most secure encryptions available. WPA3 is an improved version of WPA2. It helps make public WiFi networks safer and makes it harder for hackers to access your private network. If hackers were to access the network, they would only be able to see a limited amount of information.
What are the Drawbacks of a Mesh Network?
1) Cost
A good quality mesh WiFi system typically starts around $200 and comes with 2-3 nodes to cover most homes. Additional nodes may be needed for larger spaces to get wall-to-wall coverage. These extra nodes are usually sold separately and can range from $100 to $200 depending on the brand.
2) Complexity
Each node has a lot of responsibility. They have to transfer data and act like a router. Adding more nodes makes the system more complex, making it harder to manage and troubleshoot.
3) Latency and More Power Consumption
Given everything nodes do, they may need to draw more power to operate effectively and efficiently. In some cases, there may not be enough processing capability to handle certain tasks, causing latency.
How to Choose the Best WiFi Mesh System?
There are a lot of different mesh network manufacturers (Netgear, Asus, TP-Link, Google, etc.), each with different pros and cons. To figure out which would be the best mesh WiFi system, here are a few things you should look out for:
Mesh Network Frequency Bands
WiFi access points and WiFi-enabled devices communicate with each other through frequencies. Most Mesh networks are dual-band, meaning they use frequency bands 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band travels farther with slower speeds, while 5 GHz provides higher speeds but doesn't travel as far or penetrate obstacles as well.
Some units are tri-band, adding an extra 5 GHz or 6 GHz band, boosting capacity, throughput, and bandwidth. These might even dedicate a band for exclusive communication between nodes for smoother performance.
Recently, quad-band units have entered the market. They make use of the all-new 6 GHz band to deliver faster speeds and offer great capacity for the most data-demanding households.
Usually, older routers force you to choose between separate networks (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz). Most mesh units simplify this by unifying all frequency bands into one smart network. Your devices automatically connect to the best band (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or even 6 GHz on some models) for the best results.
Mesh WiFi Standard
Mesh systems are based on 802.11 WiFi protocols. The best mesh systems you will find are the ones that fall under the WiFi 5 (802.11ac), WiFi 6 (802.11ax), and WiFi 6E (expansion of 802.11ax) protocols.
WiFi 6 is still relatively new. It’s supposed to increase throughput speeds, have less network congestion, and provide better range performance. WiFi 6E does the same but allows access to the new 6 GHz band. Both WiFi standards are backward compatible with WiFi 5. The newer the standard, the more expensive the unit.
While newer WiFi 6 and 6E mesh systems offer the latest tech for faster speeds and better handling of multiple devices, they require newer WiFi 6 or 6E compatible devices to truly shine. If your devices are older and you aren't planning upgrades soon, a WiFi 5 mesh system might be a more practical choice.
WiFi Mesh Coverage Capabilities
Every mesh system is rated to cover a certain amount of square feet. It could be 3,000 sq ft or 9,000 sq ft. You’ll want to select a system that offers the coverage you need for your building. If additional nodes are needed to achieve desired coverage, they can be purchased separately.
Mesh Network Features
Two popular core features that help take your WiFi experience to the next level are MU-MIMO and Beamforming. MU-MIMO (multi-user, multiple-input, multiple-output) allows access points to support multiple data streams from multiple devices. Users experience substantially better download speeds. Beamforming focuses the wireless signal in the direction of the connected device rather than transmitting it in every direction. This helps improve reliability, range, speed, and reduces interference.
What is the Best WiFi Mesh Network for My Needs?
The best Mesh network for you will depend on your usage and coverage needs. Here is our top recommendation:
TP-Link Deco AX3000 WiFi 6 Mesh System
- WiFi 6 Mesh WiFi System
- Covers Up to 6,500 Sq Ft
- Connects Up to 150 Devices
- 3 Gigabit Ethernet Ports Per Deco Unit (9 total for a 3-pack)
- Supports Wired Ethernet Backhaul
- AI-Driven Mesh
- Easy Setup and Management with Deco App
- Easy Setup and Management with Deco App
With the TP-Link Deco X55 mesh WiFi system, you can blanket your home in high-performance WiFi 6, eliminating dead spots and buffering throughout up to 6500 square feet. It can connect over 150 devices and offers flexible wired and wireless network connections. The Deco app ensures a smooth setup and lets you manage your network remotely. With built-in TP-Link HomeShield, you can also benefit from network security features and parental controls.
Why Not Use a WiFi Range Extender?
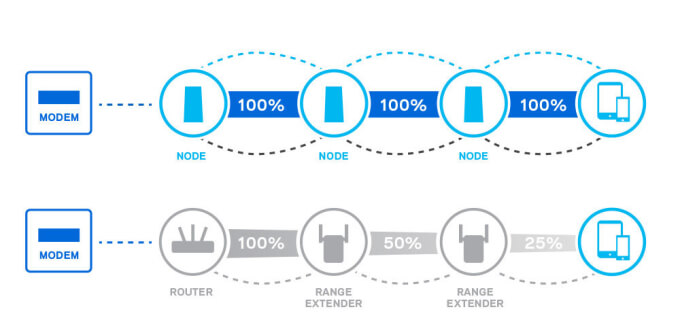
Image Source: Linksys
WiFi range extenders do extend your WiFi coverage. They wirelessly connect to your router and rebroadcast the signal by creating a second network. This can cause connection issues and diminish network performance, which doesn’t happen with a mesh network.
All mesh units are configured to a single network. Each node is optimized to cover as much area as possible while delivering the best speeds possible. Devices seamlessly connect to the closest node as you roam around your home.
To learn more, visit WiFi Extender vs. Mesh Network.
WiFi extenders tend to perform better in small areas, while mesh networks are best for mid to large areas.
- Dual Band, 5 GHz & 2.4 GHz
- Extends WiFi Coverage Up to 1,500 Sq Ft
- Connects Up to 30 Devices
- Compatible with Any WiFi Router
- Fast Ethernet Port for Wired Connection
- Access Point Mode for Wired Devices
- Supports TP-Link OneMesh for Mesh Network
The TP-Link RE315 WiFi range extender is designed to boost your existing WiFi signal, covering up to 1500 square feet and supporting connection for up to 30 devices. Apart from being universally compatible with various routers and access points, it also supports TP-Link OneMesh for creating a mesh network for seamless whole-home coverage.
Do I Need a Mesh Network?
Mesh networks are a great solution for getting rid of poor internet connections in those hard-to-reach areas, like the basement, garage, etc. However, they are not the best solution for every situation.
If you have a large home of 3,000 sq ft or bigger, a home with building material obstructions (metal walls and brick walls), or a multi-story home, you will benefit from a wireless mesh network. Using multiple nodes will help expand the coverage into every room for whole-home WiFi coverage and reduce interference caused by obstacles.
On the other hand, if you live in an apartment or a small home, and only experience dead zones or poor speeds occasionally, a mesh network may be overkill. A range extender will work just as well and will be a more cost-effective solution that can help patch up those problem areas.
FAQs
Can You Use A WiFi Extender with A Mesh Network?
Technically, you can use a WiFi extender with a mesh network to get more coverage. However, it's not recommended. Mesh networks are designed to work together seamlessly as a single system. Adding an extender creates a separate network, which causes connection drops during switches and confusion for your devices as they decide which network to connect to. For better performance and a smoother experience, stick with the mesh network nodes for extending coverage.
Do Mesh Networks Need to be Hardwired?
No, mesh networks don't require hardwiring, but it can improve performance. They function perfectly well wirelessly, but wired connections (Ethernet backhaul) between the mesh nodes and the router can offer a significant boost in speed and stability. So if you are performing bandwidth-intensive tasks like gaming or streaming, it can be useful.
Does Mesh WiFi Work Through Walls?
Walls can weaken or completely block wireless signals. When you use smart technology, like beamforming, Mesh WiFi can blast signals through walls and other WiFi signal blocking materials. However, the wall's material and thickness will affect how strong the signal is on the other side.
Can Mesh WiFi Reach Outside?
While not designed for outdoor use, a mesh network can help you extend your WiFi coverage outside. By placing a mesh node close to a window, the signal can bleed through the walls and keep you connected in your front or backyard.
How Many Mesh Nodes Do You Need for Whole-Home Coverage?
Most mesh kits come with 2-3 nodes, which is sufficient for average size homes. You have the option of adding more nodes as needed. Some mesh systems support up to 32 nodes.
Before you go and spend all your hard-earned money on 32 nodes, figure out how much coverage you need. To do that, figure out the square footage of your home and factor in the distance between floors for multi-story homes. The range of each mesh system varies between models. Make sure to check the specs on the systems that interest you. Some nodes provide more square feet of coverage than others.
Does Having Additional Mesh Nodes Create a Problem?
While having multiple mesh nodes widens WiFi coverage, there is such a thing as too many nodes. Adequate distance between nodes is very important. In most cases, deploying too many nodes will result in them being too close to each other. This will result in increased interference and decreased performance.
Contact Us
Signal Boosters is a leading provider of cell phone signal boosters for homes, vehicles, and commercial buildings. We specialize in consumer-friendly kits as well as customized RF systems for cellular, public safety two-way radio, DAS, and WiFi.
We’re here to assist with any issues you might be experiencing with poor cell service. Contact us today, or call us at 1-800-470-6777.
Interested in Learning More? Check Out Our Cellular Info Hub / WiFi Info Hub
Disclaimer: This blog contains affiliate links, which means that if you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission. However, this does not affect the integrity or quality of the recommendations provided.










